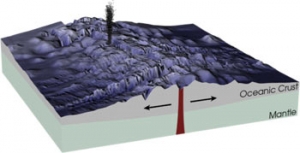
Example of a Mid-Ocean Ridge Landform:
The of mid-ocean ridge or ocean ridge picture is an exampleof the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Atlantic Ocean
A mid-ocean ridge is an undersea mountain range located where two tectonic plates are moving away from each other and magma swells from the separation.
Hot magma from below the Earth’s crust, rises between the two tectonic plates on each side of the ridge. As the magma makes contact with ocean water, it cools forming part of the Earth’s crust as it separates. Circulation of the mantel below each plate helps to spread the plates apart at the mid-ocean ridge.
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the longest, stretching for 10,000 miles. All mid-ocean ridges are connected as one continuous undersea mountain range approximately 40,000 miles long.
Mid-ocean ridges are under the oceans of the world, where two tectonic plates of the Earth’s crust are moving away from each other.
• Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Atlantic Ocean
• Southwest Indian Ridge, Atlantic and Indian Oceans
• Explorer Ridge, Pacific Ocean
• East Pacific Rise, Pacific Ocean
• Pacific-Antarctic Ridge, Pacific Ocean
Europe and Africa were once together with North and South America, and there was no Atlantic Ocean. About 140 million years ago, South America began to separate from Africa, a ridge forming between them. 80 million years ago, North America began to separate from Europe at what became the Mid-Atlantic Ridge in the North and South Atlantic Ocean.
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is 10,000 miles long and was discovered in the 19th century during the laying of the first trans-Atlantic cable. At the southern end in the South Atlantic Ocean, the Southwest Indian Ridge begins, stretching southeast and east to a point about 2000 miles south of India to join the Mid-Indian and Southeast Indian ridges.
The Explorer Ridge lies under the Pacific Ocean about 150 miles west of Vancouver Island and runs south to a point that is even with northern California where the San Andreas Fault begins. The Pacific Plate on the left moves northwest from the ridge and the Explorer Plate moves east, under the edge of the North American plate near the coast.
The East Pacific Rise is a mid-ocean ridge that begins at a point where the San Andreas Fault ends at the Salton Sea in California, north of the Mexican border. It passes under the northern Gulf of California and southwest uncer the Pacific Ocean toward Antarctica, meeting the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge.
The sea floor at the East Pacific Rise is spreading 7.5 centimeters each year, three times faster than the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The Pacific-Antarctic Ridge continues southwest and west under the South Pacific Ocean to a point south of New Zealand, separating the Antarctic and Pacific Plates.
A mountain range under the ocean where two tectonic plates separate
We want pictures and location of the lanforms around the world and we need your help. Click get started button below.
In Asia, China, India, Nepal, and Bhutan are home to one of the eight wonders of the world and one of the most beautiful mountains in the world, the Himalaya Mountains also called the Himalayas. Boasting as the world’s highest and most famous mountain peak, Mt. Everest. Within the verse of the ‘Kumarsambhava’, Sanskrit […]
Nature have provided us with fascinating landforms and features. The most often adored landforms are volcanoes. Like the perfect cone structure of Mayon Volcano in the Philippines or Mount Fiji in Japan, people look at their beauty and wonder with great appreciation to nature. Volcanoes are mountains with a very disastrous nature. Their only […]
Taal Volcano is the second most active volcano found in the province of Batangas. A complex volcano in the middle of Taal Lake and is often called an island within a lake, that is an island within a lake that is on an island as well as one of the lowest volcano in the […]
Mayon Volcano is one of the active volcanoes in the Philippines. Located in the southern part of Luzon about 473 kilometers (294 miles) from Makati Business District of the Philippines, Mount Mayon is the main landmark of the Province of Albay of Bicol Region. According to local folklore, the volcano was named after Daragang […]
The global temperature and weather is to a large extent a direct result of the sun’s effect to our planet. Together with the atmosphere and the rotation of the earth on its axis. The earth on which weather moves on has its own effect on the weather. The different landforms like mountains, volcanoes, plains, and the […]